
#Best cpu stress test haswell pro
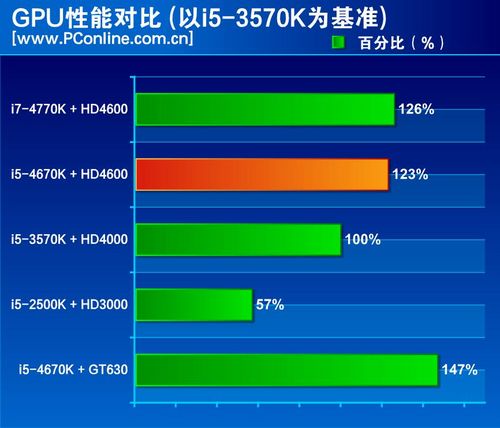
The higher models dubbed Iris 5100 and Iris Pro 5200 will actually not be available in many desktop chips, instead they will be pushed on the mobile market where they will have a bigger impact. The difference between 4200, 4600, and 4600 hasn’t been clearly stated by Intel but our guess would be clock speed. The slower models are Intel HD Graphics, HD Graphics 4200 / 4400/ 4600, and HD Graphics 5000.

There are four levels of performance denoted by the prefix “GT” but each level also have specific model names. The nomenclature is somewhat confusing however.
Each chip in their family is essentially the same chip only with a different number of sub-slices. Under the hood, the core has been redesigned to be easily scalable by using what Intel calls “sub-slices,” the essential building blocks of their graphics technology which each include 10 EU’s (Execution Units). The newest version gets support for the DirectX 11.1, OpenCL 1.2, and OpenGL 4.0 APIs, 4K resolution displays, and DisplayPort 1.2, along with a revamped version of Intel’s Quick Sync video technology. Intel’s HD graphics have come a long way and the latest evolution is nothing to sneeze at.
#Best cpu stress test haswell portable
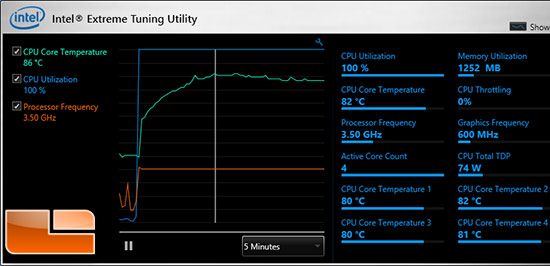
With the world moving toward portable devices, battery life appears to be one of the biggest bottlenecks to advances in consumer technology. While idle power consumption is not terribly important on desktop systems, it’s absolutely vital for the ever growing mobile market. Power regulation has been altered as Haswell has a fully integrated voltage regulator included, and lower C-States are now supported to help boost idle energy efficiency. There are several other minor improvements under the hood including increased bandwidth between the different cache levels, refined Turbo Boost frequencies. Added to the mix, as usual, are updated instruction sets, this time AVX2 and AMD’s FMA3, both of which primarily benefit floating point calculations and SIMD operations. Haswell carries the same essential design of Ivy Bridge, including all the key elements from its predecessor such as 22 nm Tri-Gate transistors, Turbo Boost, Quick Sync video transcoding, and a host of virtualization and management features. 1.4 billion transistors on a 177 mm² die.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
